Why Consider Sustainable Renewable Energy?
Potential investment benefits may include:
- Attractive risk-adjusted returns
- Capital appreciation
- Low correlation to traditional equity and fixed-income market
- Portfolio diversification
- Tax-advantaged distributions
- Access to the rapidly growing and essential renewable energy sector
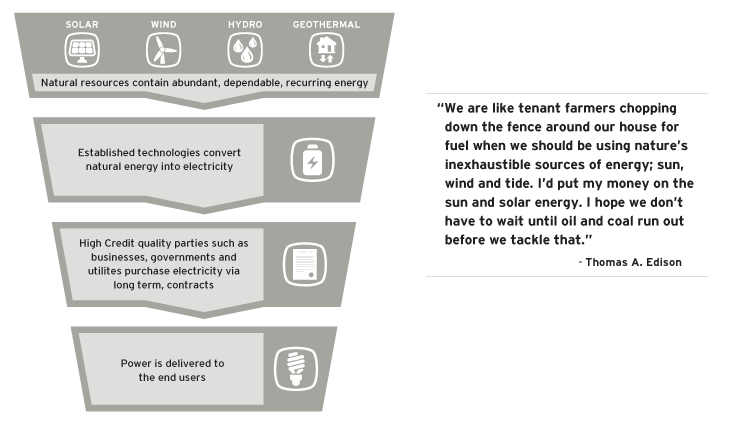
Creating Electricity
Renewable power plants use established technologies to convert the energy from natural resources—the sun, wind, moving water, and geothermal heat—into electricity. Electricity is then typically sold to creditworthy entities such as businesses, utilities and/or governments via long-term contracts. Furthermore, unlike traditional power plants, renewable power plants are not subject to the changing global markets for oil, coal, and natural gas. Nor do they require the acquisition of these raw materials to create electricity. When the sun shines or the wind blows, electricity can be created and sold.
The Renewable Energy Opportunity
In addition to the depletion of limited natural resources such as traditional fossil fuels, there are several other factors contributing to the rapid growth in the renewable energy marketplace.

1 Source: ExxonMobil 2013 Outlook For Energy: A View To 2040.
2 Source: U.S. Energy Information Administration, 2013.
3 Source: Solar Energy Industries Association and GTM Research Q3 2012: Bloomberg New Energy Finance 2012.

